The lifespan of solar panels depends a lot on the materials used to seal them. That's why researchers spend a lot of time studying these materials. A comparative analysis of the aging resistance of the four mainstream encapsulation films currently on the market: Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), POE, EPE, and PVB. PolyVinyl Butyral Film (PVB film) exhibits excellent aging resistance, while EVA film exhibits good initial performance but relatively poor aging resistance.

1. Four Mainstream Encapsulation Films
EVA film: Made from ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer resin, it is the largest market share photovoltaic module encapsulation material. Vinyl acetate groups are introduced through high-pressure polymerization. The vinyl acetate content affects film performance and is typically between 28% and 33%. EVA film technology is mature and relatively low-cost. As a photovoltaic module encapsulation film, it offers the following advantages:
- Strong adhesion to photovoltaic glass, solar cells, and backsheets
- Good melt flowability and low melting temperature
- High light transmittance
- Excellent flexibility, minimizing damage to solar cells during lamination
- Excellent weather resistance
POE film: A random copolymer elastomer formed from ethylene and 1-octene, it features a low melting point, a narrow molecular weight distribution, and long chain branches. In the ethylene-octene copolymer system, octene units can be randomly attached to the ethylene backbone, resulting in excellent mechanical properties and light transmittance.
Excellent moisture vapor barrier properties: Its moisture vapor transmission rate is approximately 1/8 that of EVA. Its stable molecular chain structure results in a slow aging process, providing better protection for solar cells from moisture corrosion in high-temperature and high-humidity environments and enhancing PID resistance in solar modules.
Excellent weather resistance: The molecular chain contains no hydrolyzable ester bonds, preventing the generation of acidic substances during aging.
EPE Co-extruded Film: This encapsulation film was developed to address the application challenges of POE films. POE films are prone to additive precipitation during lamination, resulting in slippage during use and affecting product yield. Therefore, EVA and POE are co-extruded in multiple layers to create EVA/POE/EVA multilayer co-extruded films.
This film combines the advantages of both materials: it possesses the water barrier and PID resistance of POE with the high adhesion of EVA.
Process control is challenging: Polyolefin elastomers are non-polar molecules, while ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers are polar molecules. The two resins exhibit significant differences in cross-linking reactivity, melt viscosity, and shear melt heating rate, making it difficult to effectively control quality through a simple co-extrusion process.
PVB Film: This film offers significant advantages in photovoltaic module encapsulation, particularly for building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) modules. This thermoplastic polymer is formed by the acid-catalyzed condensation of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) generated by the hydrolysis or alcoholysis of polyvinyl acetate and n-butyraldehyde. It is recyclable and reprocessable, and does not require a cross-linking reaction.
Strong Adhesion and Mechanical Properties: It exhibits strong adhesion to glass and high mechanical strength.
Excellent Aging Resistance: It exhibits exceptional environmental aging resistance, making it more resilient for outdoor use and capable of lasting up to four years without compromising performance. Its adhesion to glass and impact resistance are superior to those of EVA film, and its aging resistance is also superior to that of EVA film.
2. Aging Resistance - UV Accelerated Aging Test
The UV accelerated aging test verifies atmospheric light aging resistance. After lamination, the prepared materials are placed in a UV aging chamber under controlled test conditions. After aging, the peel strength and yellowing index of the film against glass are measured.
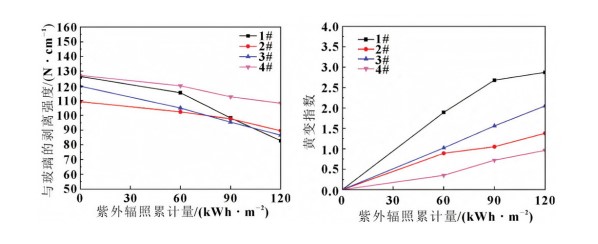
UV radiation damages the film's adhesive properties, but the effect is less severe than in high temperature and high humidity environments. EVA exhibits significant yellowing after UV irradiation. Peel Strength Change: UV irradiation does affect the peel strength between the film and glass to some extent, but the effect is less pronounced than in high-temperature, high-humidity environments. Different films exhibit different peel strength change trends after UV irradiation. For example, samples 1# (EVA), 2# (POE), 3# (EPE), and 4# Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB) all show a decrease in peel strength after UV irradiation, but the degree of decrease varies.
Yellowing Index Change: EVA exhibits significant yellowing after UV irradiation. This is because residual crosslinkers in the EVA decompose under the influence of light, generating reactive free radicals that react with the antioxidant (UV absorber) to form chromophores. The yellowing index of other films also changes after UV irradiation, but to a lesser extent than that of EVA.
3. Aging Resistance - High-Temperature, High-Humidity Aging Test
The laminated samples were placed in a constant temperature and humidity chamber at a temperature of (85±2)°C and a relative humidity of 85%±5% for 1000 hours.
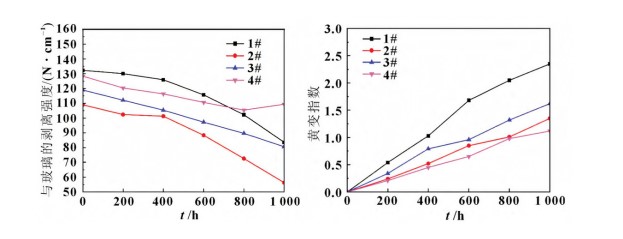
The peel strength of all four samples against glass decreased after hygrothermal aging. PVB exhibited superior hygrothermal aging resistance, while EPE fell between EVA and POE. EVA was more susceptible to yellowing under high temperature and high humidity conditions.
Peel Strength Change: The peel strength of samples 1#, 2#, 3#, and 4# against glass decreased after hygrothermal aging, and this continued to decline with increasing hygrothermal aging time.
Yellowing Index Change: The yellowing index of all samples increased with increasing hygrothermal aging time, with EVA showing the largest increase, indicating that EVA is more susceptible to yellowing under high temperature and high humidity conditions.
4. Aging Resistance - Humidity-Freeze Aging Test
Laminated specimens were placed in a temperature-humidity cycling test chamber. The cycle conditions were characterized by specific temperature and humidity variations, as shown in the figure below. The number of cycles was 20.
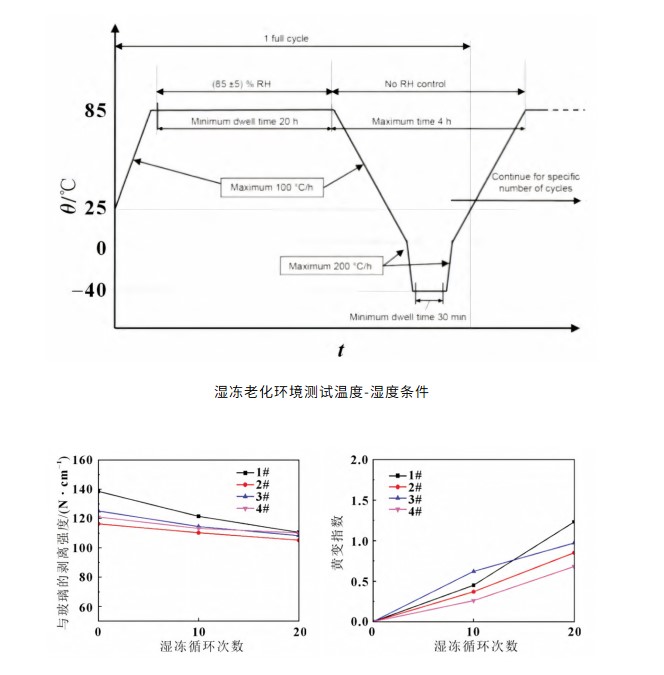
Peel Strength Change: As shown in the figure, the humidity-freeze cycle had little effect on the peel strength between films 1#, 2#, 3#, and 4 and the glass. The peel strength of the four films remained relatively stable during the humidity-freeze cycle, with no significant decrease.
Yellowing Index Change: The four films showed low yellowing after the humidity-freeze cycle, demonstrating that they maintain high performance despite frequent temperature fluctuations and exhibit good resistance to yellowing. Their optical properties remained relatively stable in environments with high humidity and large temperature fluctuations.
Mechanical tests showed that PVB has the best properties, while EVA is mechanically stronger than POE, with EPE in between. Overall, PVB film resists aging best, while EVA is good at first but ages faster. EVA is still popular because it's affordable. As tech gets better, POE and EPE will likely become more common alongside EVA, giving more choices for sealing solar panels.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com