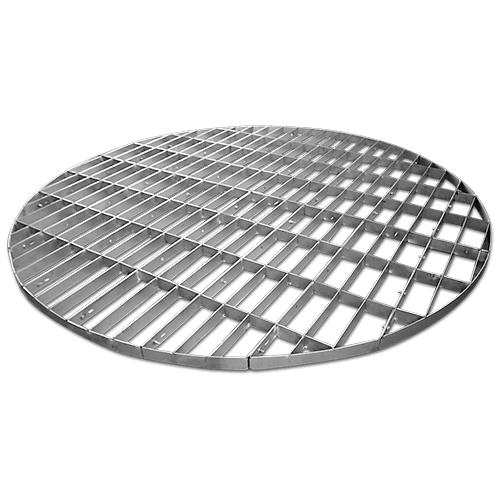
Support Plate:
-
Design:
- Flat or slightly curved plates with openings (holes, slots, or grids) to allow the passage of gas and liquid.
- Typically made from metal, plastic, or composite materials.
-
Function:
- Primary Role: To provide a stable base for the packing material and distribute the weight evenly.
- Flow Distribution: Ensures uniform distribution of gas and liquid across the packing bed.
- Drainage: Allows liquid to drain effectively while preventing excessive hold-up or flooding.
-
Applications:
- Used in both random and structured packing systems.
- Suitable for a wide range of industries, including chemical, petrochemical, and environmental.
-
Advantages:
- Simple and robust design.
- Provides excellent support and drainage capabilities.
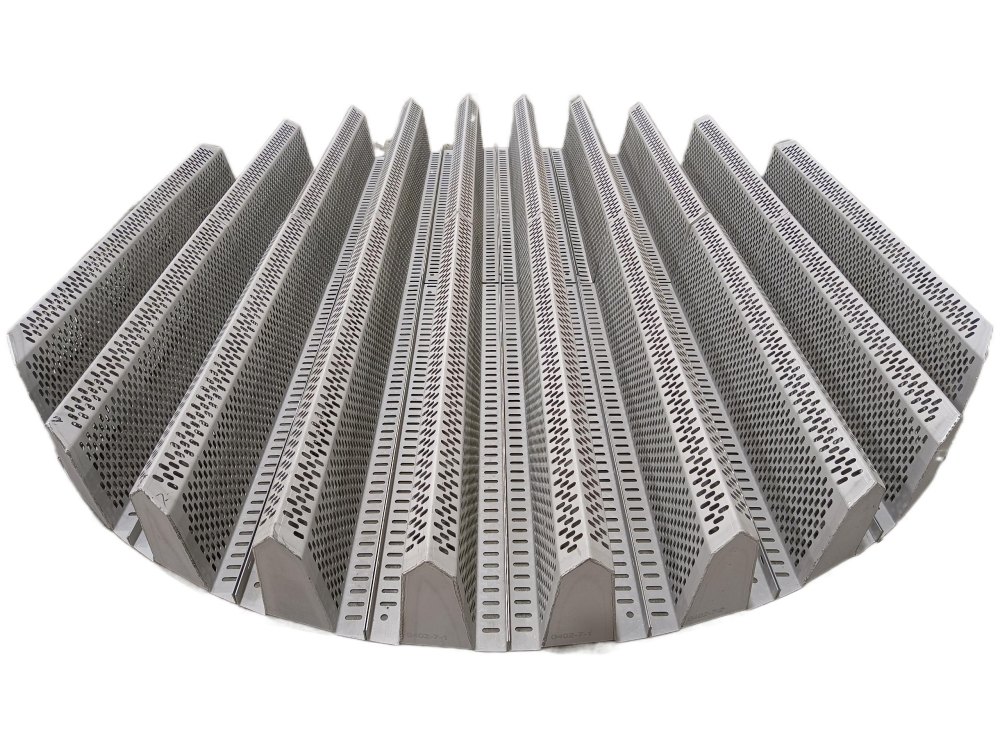
Hump Support:
-
Design:
- Curved or arched plates with a "hump" shape, often with openings for gas and liquid flow.
- Made from materials such as metal or plastic.
-
Function:
- Primary Role: To support the packing material while minimizing pressure drop and improving liquid distribution.
- Enhanced Drainage: The hump shape facilitates better liquid drainage and reduces the risk of liquid pooling.
- Gas Flow Optimization: The design allows for smoother gas flow, reducing resistance and energy consumption.
-
Applications:
- Commonly used in columns with high liquid flow rates or where minimizing pressure drop is critical.
- Ideal for applications involving random packing.
-
Advantages:
- Improved liquid and gas distribution compared to flat support plates.
- Lower pressure drop, leading to energy savings.
- Reduces the risk of flooding and channeling.
Key Differences:
-
Design:
- Support plates are typically flat or slightly curved, while hump supports have a distinct arched or hump-like shape.
-
Pressure Drop:
- Hump supports are designed to minimize pressure drop more effectively than flat support plates.
-
Liquid Drainage:
- Hump supports offer better liquid drainage due to their arched design, reducing the risk of liquid hold-up.
-
Application Specificity:
- Support plates are more versatile and widely used, while hump supports are often chosen for specific applications requiring optimized flow and drainage.
Comparison Summary:
| Feature | Support Plate | Hump Support |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Flat or slightly curved | Arched or hump-shaped |
| Pressure Drop | Higher compared to hump supports | Lower |
| Liquid Drainage | Good | Excellent |
| Applications | General-purpose, wide range | High liquid flow, low pressure drop |