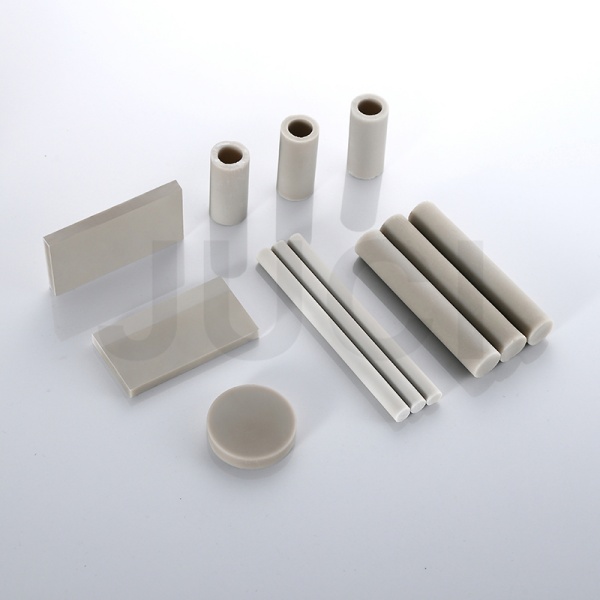
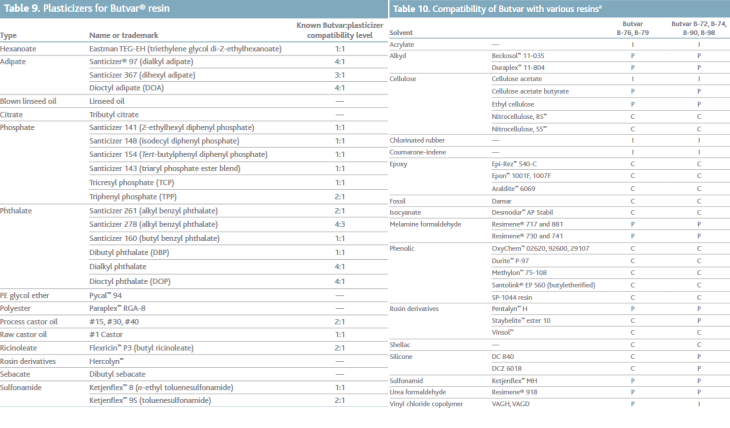
With the rise and application of power devices, especially third-generation semiconductors, semiconductor devices are gradually evolving toward high power, miniaturization, integration, and multifunctionality. This places higher demands on the performance of packaging substrates. Ceramic substrates, with their high thermal conductivity, excellent heat resistance, low thermal expansion coefficient, high mechanical strength, good insulation, corrosion resistance, and radiation resistance, are widely used in electronic device packaging.
So, between aluminum nitride (AlN) and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), which is the most promising packaging material?

Requirements for Ceramic Substrate Materials
1、High thermal conductivity to meet heat dissipation needs.
2、Excellent heat resistance for high-temperature applications (above 200°C).
3、Matching thermal expansion coefficient to reduce thermal stress between the chip and substrate.
4、Low dielectric constant for high-frequency performance, reducing signal delay and improving transmission speed.
5、High mechanical strength to withstand mechanical demands during packaging and application.
6、Good corrosion resistance to endure strong acids, alkalis, boiling water, and organic solvents.
7、Dense structure to meet hermetic packaging requirements for electronic devices.
Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
Si₃N₄ ceramic substrates have an elastic modulus of 320 GPa, a flexural strength of 920 MPa, a thermal expansion coefficient of only 3.2 × 10⁻⁶/°C, and a dielectric constant of 9.4. They exhibit high hardness, strength, low thermal expansion, and excellent corrosion resistance.
Initially, due to the complex crystal structure of Si₃N₄, which causes significant phonon scattering, its thermal conductivity was considered low (15–30 W/(m·K)), making it suitable only for applications like bearing balls and structural components. However, research later revealed that the low thermal conductivity was mainly due to lattice defects and impurities, and it was predicted that its theoretical thermal conductivity could reach up to 320 W/(m·K). Subsequent studies optimized the manufacturing process, significantly improving the thermal conductivity of Si₃N₄ ceramics, which has now reached 177 W/(m·K).
Additionally, compared to other ceramic materials, Si₃N₄ exhibits outstanding advantages, particularly in high-temperature environments, where it demonstrates excellent thermal stability, chemical inertness to metals, ultra-high hardness, and fracture toughness. The flexural strength and fracture toughness of Si₃N₄ ceramics are more than twice those of AlN, making Si₃N₄ substrates far superior in reliability.
Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
AlN is one of the few materials that combines high thermal conductivity with excellent electrical insulation.
Its advantages include:
High thermal conductivity—Theoretical thermal conductivity at room temperature can reach up to 320 W/(m·K), 8–10 times that of alumina ceramics. In practice, its thermal conductivity can reach 200 W/(m·K), facilitating heat dissipation in LEDs and improving performance.
Low thermal expansion coefficient—Theoretical value is 4.6 × 10⁻⁶/K, close to that of commonly used LED materials like Si and GaAs. Its thermal expansion behavior is also similar to that of Si. Additionally, AlN has a lattice structure matching that of GaN, which is crucial for high-performance power LEDs.
Wide bandgap (6.2 eV)—Excellent insulation properties eliminate the need for additional insulation treatment in high-power LED applications, simplifying the process.
High hardness and strength—Due to its wurtzite structure and strong covalent bonds, AlN exhibits good mechanical properties. It also has excellent chemical stability and high-temperature resistance, remaining stable in air up to 1000°C and in vacuum up to 1400°C, making it suitable for high-temperature sintering and corrosion-resistant applications.

Conclusion
Among existing ceramic substrate materials, Si₃N₄ has the highest flexural strength and wear resistance, making it the best in terms of comprehensive mechanical properties. Its extremely low thermal expansion coefficient also makes it a highly promising material for power device packaging. However, its complex manufacturing process, high cost, and relatively low thermal conductivity limit its use to applications requiring high strength but moderate heat dissipation.
On the other hand, AlN excels in almost all aspects, particularly in thermal conductivity, which is crucial for electronic packaging. The main drawback is its high cost due to expensive raw materials and processing. However, as AlN production technology advances, costs are expected to decrease, paving the way for widespread adoption in high-power LED applications.
Which material do you think will dominate the future of high-power electronics?
About Xiamen Juci Technology
As the top aluminum nitride (AlN) powder manufacturer in China, Xiamen Juci Technology specializes in high-purity, high-performance AlN materials for advanced electronic applications. Our AlN powder and ceramics deliver exceptional thermal conductivity (up to 200 W/m·K), superior electrical insulation, and outstanding mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-power electronics, semiconductor packaging, LED cooling, and next-generation 5G/EV systems.
Media Contact:
Xiamen Juci Technology Co., Ltd.
Phone: +86 592 7080230
Email: miki_huang@chinajuci.com
Website: www.jucialnglobal.com