MDI is one of the key components used in the production of TPUs. It serves as the isocyanate component, reacting with polyols to form the polyurethane segments of TPU.
The selection of MDI type and the ratio of MDI to polyols can affect the physical properties and performance characteristics of the TPU, including its low-temperature behavior. TPU formulated with a higher proportion of MDI generally have a higher density of hard segments, which can enhance the stiffness and rigidity of the material. This, in turn, can make the TPU more prone to embrittlement at low temperatures.
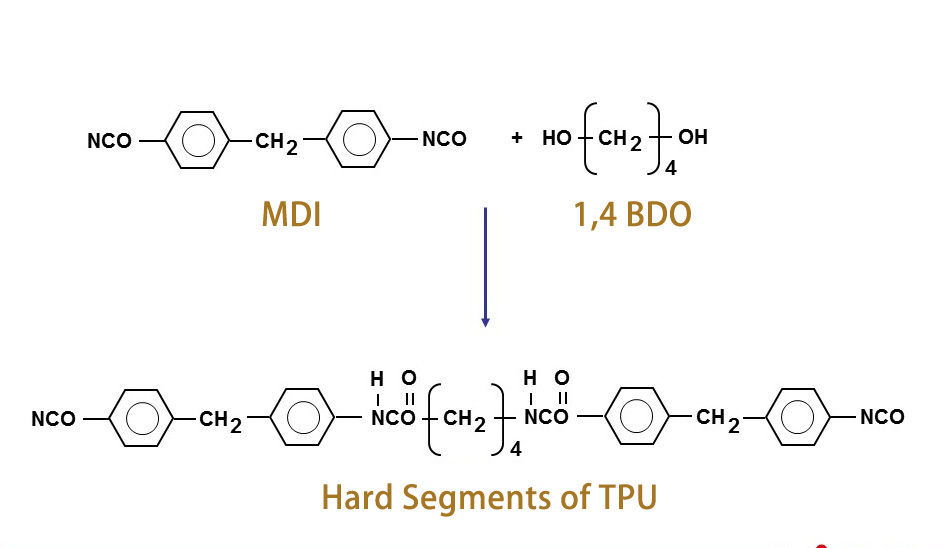
Therefore, the proportion of MDI in TPU formulations is an essential factor to consider when aiming for specific low-temperature performance requirements. It's crucial to optimize the MDI-to-polyol ratio to achieve the desired balance between hardness, flexibility, and resistance to embrittlement at low temperatures.
