Introduction
With the growing global demand for renewable energy, wind power, as a clean and renewable energy source, is increasingly gaining attention and preference from various countries. As one of the core components of wind power generation systems, the performance and quality of wind turbine blades directly affect the overall system’s generation efficiency and operational stability. The blades are key components of wind turbines, characterized by large dimensions, complex shapes, high precision requirements, and demanding strength, stiffness, and surface smoothness.
Wind Turbine Blade Composite Materials
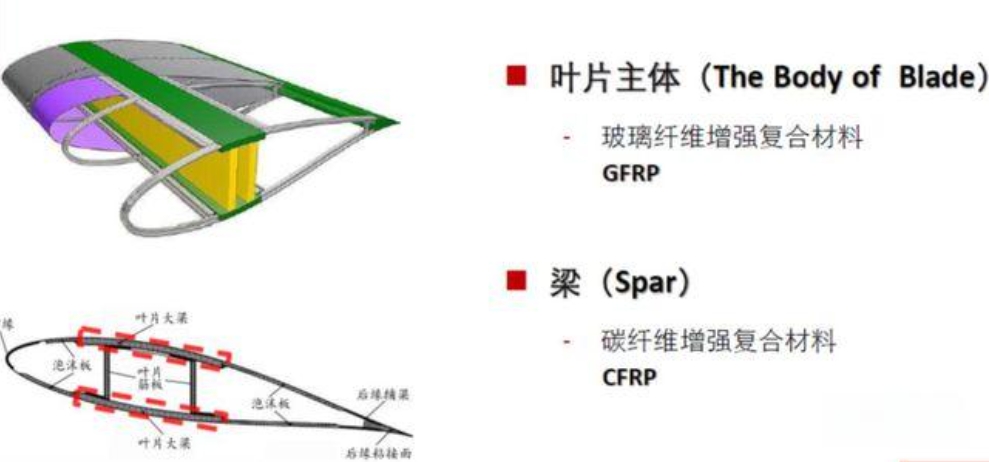
Wind turbine blades have a hybrid structure, mainly consisting of components such as the skin, spar cap, and ribs. A variety of composite materials are used in the manufacturing of wind turbine blades, with fiber-reinforced composites being a notable type. Fiber-reinforced composites are made of fibers and resin matrices, offering excellent properties such as high strength, high modulus, light weight, and corrosion resistance. Applying fiber-reinforced composites in the manufacturing of wind turbine blades can significantly enhance the blades' strength and stiffness, while also reducing their weight and improving generation efficiency.
Commonly Used Composite Materials for Wind Turbine Blades
As a critical component of wind power equipment, composite materials play an essential role in the design and manufacturing of large wind turbine blades. Advancements in composite materials technology are significant for improving the performance of wind power equipment, reducing costs, and promoting the sustainable development of the wind power industry. The commonly used composite materials for wind turbine blades include Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GFRP), Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP), and Aramid Fiber Reinforced Plastic (AFRP).
Among them, GFRP dominates the manufacturing of non-structural components of wind turbine blades due to its low cost and good processability. CFRP, with its excellent mechanical properties and design flexibility, has become the material of choice for manufacturing structural components of wind turbine blades. AFRP, which offers performance characteristics between GFRP and CFRP, is used in local reinforcement and strengthening of wind turbine blades.

Manufacturing Processes of Composite Materials for Wind Turbine Blades
Composite materials offer numerous advantages in the manufacturing of wind turbine blades. The main manufacturing processes include hand lay-up molding, pre-preg molding, pultrusion, fiber winding, resin transfer molding (RTM), and vacuum infusion molding, among others.
Advantages of Composite Materials for Wind Turbine Blades
With the rapid development of the wind power industry, composite material wind turbine blades are evolving towards more complex, larger, and lighter designs. Various processes and materials are being applied in the manufacturing of wind turbine blades. Depending on the specific characteristics of the blades, selecting the appropriate processes and materials is crucial to achieving low-cost, high-quality wind turbine blades.
Composite materials, with their light weight, high strength, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance, have become the ideal choice for large wind turbine blades. They not only improve the performance and efficiency of the blades but also promote the sustainable development of the wind power industry. In the future, with the development and application of new composite materials, the integration of digital design and manufacturing technologies, and the widespread adoption of environmentally friendly and sustainable development concepts, the use of composite materials in large wind turbine blades will become even more widespread, driving the sustainable growth of the wind power industry.
